Research & Development: Driving Innovation Through New Products, Prototyping, Feasibility Studies & Continuous Improvement
In today’s hyper-competitive business landscape, organizations cannot rely solely on past successes to secure their future. Markets evolve, technologies disrupt entire industries, and customer expectations continue to rise. To stay ahead, companies must embrace Research and Development (R&D) as a cornerstone of their growth strategy. Far beyond being a cost center, R&D has become a driver of innovation, efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
Whether it is about creating new products, testing ideas through prototyping, validating concepts via feasibility studies, or enhancing existing offerings through continuous improvement, R&D lays the foundation for meaningful progress. This blog explores these pillars of R&D in depth and highlights their role in shaping successful organizations.
What is Research & Development (R&D)?
At its core, Research and Development refers to the systematic process of exploring new knowledge, experimenting with ideas, and applying findings to create or improve products, services, and processes...
The Role of New Products in R&D
One of the most visible outcomes of R&D is the development of new products. Companies invest heavily in this area because innovation directly correlates with market relevance...
- Changing Consumer Needs – Customers demand faster, smarter, and more sustainable solutions.
- Technological Advancements – Breakthroughs like AI, IoT, and biotechnology create new opportunities.
- Competitive Pressure – Staying ahead requires differentiation in features, design, and performance.
- Regulatory & Environmental Requirements – Compliance often leads to new, improved products.
Prototyping: Turning Ideas Into Reality
Innovation cannot thrive on ideas alone. Prototyping bridges the gap between conceptual thinking and practical implementation...
- Identifies Design Flaws Early – Saves time and cost by catching issues before full-scale manufacturing.
- Enhances User Feedback – Customers or stakeholders can interact with prototypes and suggest improvements.
- Accelerates Decision-Making – Provides a visual and functional representation to guide further development.
- Supports Investor Buy-In – A tangible prototype makes funding pitches more persuasive.
Feasibility Studies: Assessing Viability Before Execution
Before investing significant resources in development, organizations must evaluate whether an idea is practical, profitable, and sustainable. That’s where feasibility studies come in...
- Technical Feasibility – Do we have the technology, skills, and infrastructure to build it?
- Financial Feasibility – Will the costs be justified by expected returns?
- Market Feasibility – Is there enough demand for the product?
- Operational Feasibility – Can the organization integrate and sustain the product effectively?
- Legal & Environmental Feasibility – Does it comply with regulations and sustainability standards?
Continuous Improvement: Sustaining Long-Term Success
While developing new products and prototypes garners excitement, continuous improvement ensures that existing products and processes remain relevant and competitive...
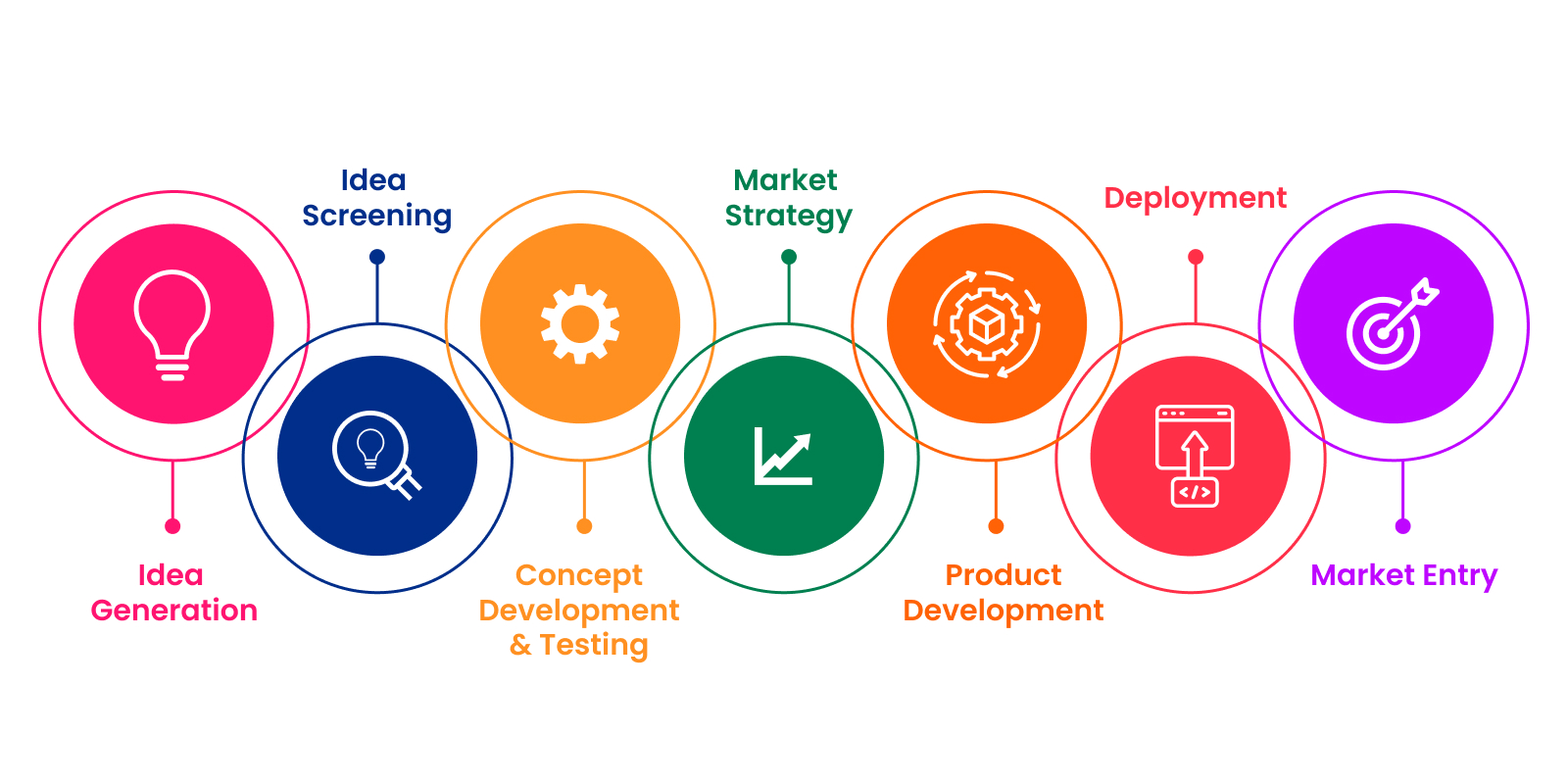
Integration of R&D: A Holistic Approach
The four pillars—new products, prototyping, feasibility studies, and continuous improvement—are not isolated steps but interconnected parts of a cyclical R&D process...
- Idea Generation → Brainstorming and research.
- Feasibility Study → Assessing whether the idea is viable.
- Prototyping → Creating tangible models for testing.
- Product Development & Launch → Bringing it to market.
- Continuous Improvement → Refining and upgrading over time.
Challenges in R&D
- High Costs – Research, prototyping, and testing require significant investment.
- Uncertainty – Not all projects yield successful outcomes.
- Time-Intensive – R&D often involves long lead times.
- Talent Requirements – Needs skilled professionals across multiple disciplines.
Future Trends in R&D
- AI-Driven R&D – Using artificial intelligence for predictive modeling, faster prototyping, and data-driven insights.
- Sustainability Focus – Developing eco-friendly products and green technologies.
- Open Innovation – Collaborating with universities, startups, and other industries.
- Digital Twins & Simulation – Creating digital replicas of products for real-time testing.
- Personalization – Customizing products based on customer data and preferences.
Conclusion
Research and Development is no longer optional; it is a strategic necessity. By focusing on new product development, leveraging prototyping, validating through feasibility studies, and committing to continuous improvement, organizations can secure their place in an ever-changing market...